Urinary System
Nephrectomy
Nephrectomy is a common surgical procedure in medical practice. It may involve partial nephrectomy or total nephrectomy, removal of one kidney, including the adrenal glands and lymph nodes, or removal of both kidneys, called radical nephrectomy.
Surgical Techniques
The first method is called conventional open surgery, which means traditional surgery using the principle of major surgery.
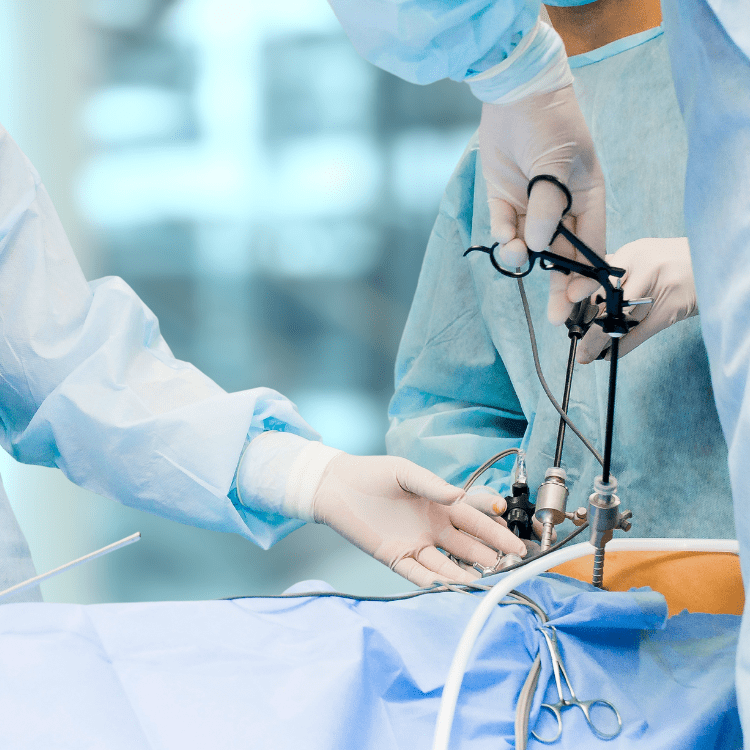
The second method is laparoscopic surgery, which is suitable for single kidney surgery. In the first method, the surgeon makes an 8-12 inch incision on the skin on the side of the body to minimize the impact on the internal organs of the abdomen. Sometimes the incision may extend to the front or back, depending on the case. In laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon makes four small incisions on the abdominal wall to insert surgical instruments, including a camera and various surgical instruments. After the kidney surgery is complete, the doctor will consider opening another wide incision to remove the kidney from the body.
Both conventional open nephrectomy and laparoscopic nephrectomy are performed under general anesthesia. The advantages of laparoscopic nephrectomy are that the patient experiences less pain after surgery, the wound heals faster, and there is less scar tissue from the surgery. However, the disadvantages are that the surgery takes longer and requires only an experienced surgeon. In the near future, a robotic kidney surgery technique has been developed, called robotic surgery, which is becoming more widely used in many countries.
Kidney surgery in various cases
- In cases of cancer, one kidney, including the adrenal gland and nearby lymph nodes, must be surgically removed.
- In cases where kidney tissue is damaged by infection, kidney stones, renal cysts, or urinary tract obstruction
- In cases where the patient has severe hypertension due to renal artery stenosis, which causes kidney tissue damage, it is easier to control blood pressure after kidney surgery.
- In cases where the patient has been in an accident, such as a car accident
- In cases of kidney transplantation
Preparing for surgery
- Avoid taking aspirin and all blood-thinning drugs for at least one week before surgery.
- Do not eat or drink after midnight the day before surgery to prevent vomiting during surgery.
- Review the history of drug allergies, past illnesses and surgeries.
- In case of suspicion of pregnancy, the doctor must be notified immediately.
Patient follow-up
After the doctor allows you to go home and makes an appointment for a week to check the condition of the surgical wound and evaluate the initial surgical results, in general, for conventional open surgery, the doctor will let you recover for about 6 weeks. For laparoscopic nephrectomy, the recovery time is about 4 weeks.
Possible complications
- Danger to nearby organs, such as intestines, liver, spleen, pancreas
- Bleeding in the abdomen or at the surgical wound
- A hole in the lung during surgery, causing the lung to collapse
- Reduced lung and respiratory function after surgery
- Surgical wound infection
- Kidney function may decrease somewhat in the early period after surgery
- Danger to nerves near the surgical wound
- Hernia at the surgical wound
- Categories
- Urinary System





