Men's Specialty
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Men over 45 years old, the prostate gland is usually enlarged to some extent, which is a change according to the body. Patients will not have any symptoms until they are over 55 years old. Some men may have an enlarged and hard prostate gland, press on the urethra, and the bladder muscles are not strong enough to squeeze against the pressure of the prostate gland, causing urinary tract obstruction. This disease may be found in about 10% of elderly men.
Prostate
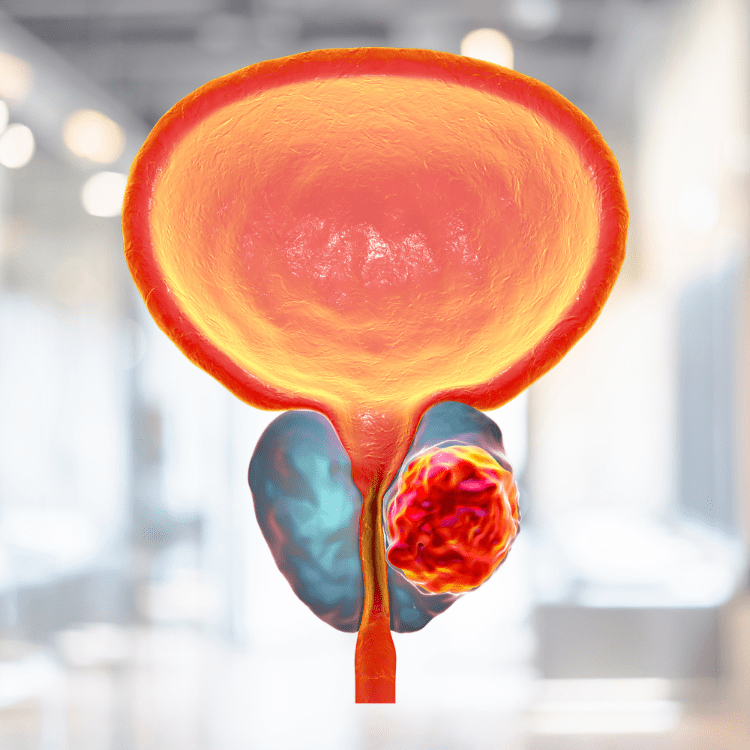
The prostate gland is one of the male reproductive organs, attached to the bladder and surrounding the upper part of the urethra. It looks like a kaolin, 4 centimeters wide, 3 centimeters long, and 2 centimeters thick. Its function is to create fluids and substances that nourish sperm to be strong so that sperm are complete to perform the function of reproduction.
Prostate diseases are divided into 3 types:
- Bladder enlargement, found in 80%
- Prostate cancer, found in 18%
- Prostatitis, found in 2%
- Enlarged prostate It is a disease found in men aged 50 years and over.
It is an abnormality that has a growth in both the size and number of prostate cells more than normal, causing the prostate gland to enlarge. And the position of the prostate gland, which is around the urethra, will squeeze the urethra to be narrow, flat and long, causing blockage in the urinary tract, resulting in inconvenient urine flow.
Causes of prostate enlargement
The cause of the disease has not been clearly concluded, but it is believed to be related to age and an imbalance of male and female hormone levels in the blood as people get older. Testosterone levels tend to decrease in older men.
Symptoms of prostate enlargement
Symptoms due to the enlarged prostate gland causing blockage of the urinary tract and bladder neck, resulting in abnormal urination as follows:
- Frequent urination both day and night. The need to urinate so often that sometimes I even pee before reaching the bathroom.
- Difficulty urinating, having to strain, urine stream not flowing or weak
- It takes a long time to urinate each time, and when it does, it takes a long time to finish urinating.
- Incomplete urination as if there is still urine remaining
- Sometimes the symptoms become so severe that you cannot urinate.
Generally, the initial symptoms of enlarged prostate are frequent urination and difficulty in urinating. As the disease progresses, the symptoms of difficulty urinating, having to strain to urinate and taking a long time to empty the bladder will gradually increase. Eventually, the patient may not be able to urinate.
Complications
- There is blood in the urine because the blood vessels in the prostate gland have ruptured due to the need to strain to urinate.
- Cannot urinate
- There is urine retention due to incomplete urination.
- Urinary tract infection occurs due to urine remaining in the bladder.
- There may be stones forming in the bladder.
- Renal failure is the most dangerous condition, occurring in no more than 10% of cases.
Diagnosis
- Ask about your history and ask about your urinary symptoms, including the time it started.
- Using a questionnaire on urination symptoms that can be calculated as a score, it is divided into 3 groups: mild, moderate, and severe symptoms, respectively.
- The doctor will examine your rectum to feel your prostate to see how big it is.
- Measuring the strength of urination, which requires urination in a special device that can measure the strength of urine.
- Urethroscopy to see if the prostate is really enlarged and to see if there are any complications in the bladder, such as stones.
- Measuring the amount of urine remaining in the bladder.
- Measuring the size and appearance of the prostate using an ultrasound machine inserted into the rectum.
- Blood test to check the results of the prostate gland (PSA) to help differentiate between prostate cancer.
Treatment of enlarged prostate
- Conservative treatment is used in cases where symptoms are mild and there are no complications.
- There are two types of medication used:
- Drugs that reduce the size of the prostate gland include 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which stimulate the prostate gland to enlarge. Taking this enzyme inhibitor may also cause the prostate gland to shrink.
- Drugs that reduce the spasm of the smooth muscle in the prostate gland, reducing the tightness of the prostate gland, will improve urination, such as alpha-blockers.
- Surgery is used in cases where symptoms are severe or there are complications. There are many types of surgery, but the most popular method is to insert instruments through the urethra and remove the prostate through the urethra using electricity. This method is called Transurethral resection of the prostate (TUR-P). If the prostate is very large, surgery through the abdomen may be necessary.
- Treatment involves heating the prostate tissue. Heat can come from various sources, including microwaves, radiofrequency, ultrasound, or laser. Heat causes the prostate to shrink and the urinary tract to widen, which is known to have fewer complications and shorter hospital stays.
- Categories
- Men's Specialty